A comprehensive guide to select hardware for Edge Computing solutions
The right hardware for Edge Computing: How to make the best choice
Edge computing is a technology that allows data to be processed close to the source instead of being sent to central data centers. This allows for faster response times, lower latency and increased data security. Fast and efficient data processing and transmission are critical to business success in today’s digital world.
The development and implementation of Edge infrastructures, is a complex process that involves many challenges and requirements. Once a use case is in place, it is a matter of implementing the idea as quickly as possible.
This blog post is intended to serve as an orientation and all-round view for your own Edge infrastructure and to show which things should already be considered during a proof-of-concept (PoC) – from the selection of the Edge gateway to integration in the cloud.
The right choice of hardware platform for successful Edge computing applications
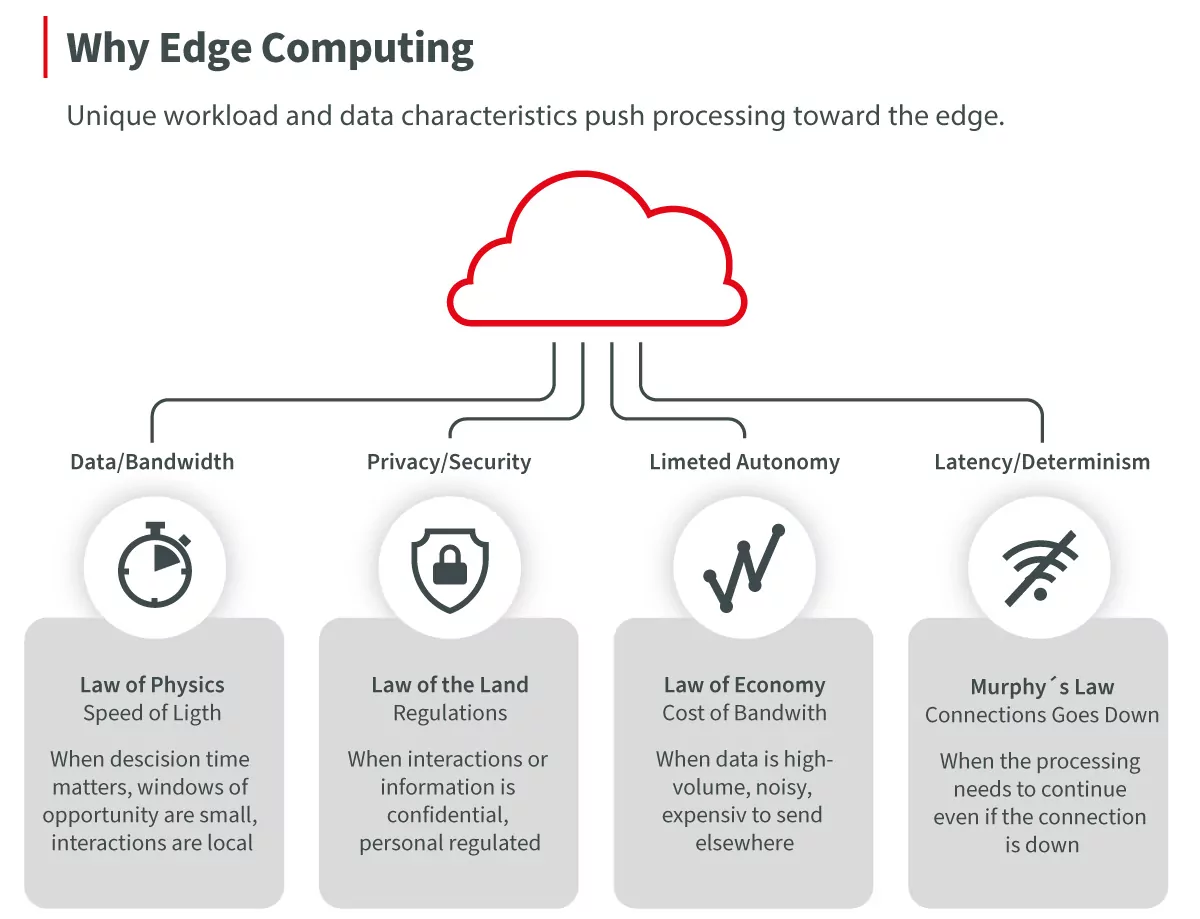
Choosing the right hardware platform for successful Edge computing applications is critical. A wrong decision can lead to limitations in performance, increased costs and security risks. In this context, several factors and components that affect performance at the edge must be considered. These include processor speed, memory, network connectivity, power consumption and ambient temperature. Careful analysis and evaluation of these factors can help to make the right hardware selection and optimize the performance of the Edge computing application.
Overall, when selecting Edge devices, make sure that the performance of the entire Edge gateway is sufficient to meet the requirements of the application at the edge. An IoT gateway that is too weak can cause delays and even failures, which can affect operations. Additionally, the platform should be scaled so that future use cases can be reloaded on the same platform and no new hardware needs to be installed in the field.
Important interfaces for Edge infrastructures: what you should know
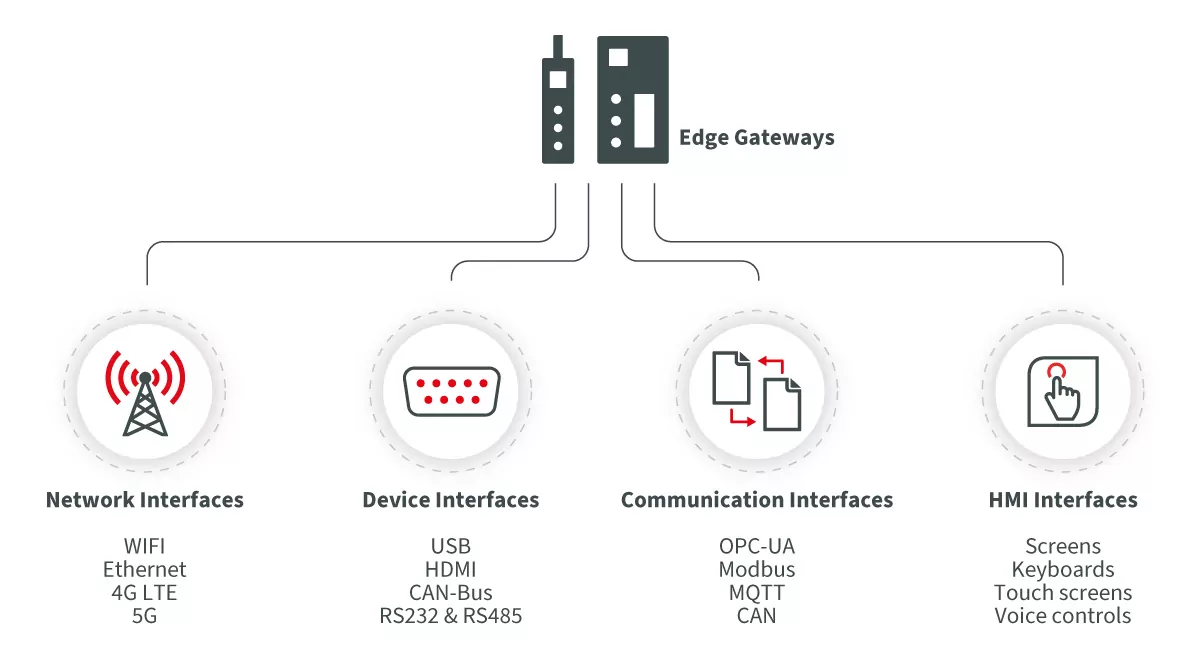
In an Edge infrastructure, different components must communicate with each other to achieve optimum performance. Interfaces play a crucial role here, as they enable the exchange of data and information between components. Important interfaces in the implementation of Edge computing applications should be carefully selected and evaluated to ensure smooth communication between components.
The selection of the right interfaces depends on various factors, such as the type of application, bandwidth, latency requirements and range. A sound knowledge of the different interfaces and their characteristics can help ensure a successful implementation of Edge computing applications.
- Network interfaces: These interfaces enable communication between IoT gateways and other devices or networks. These include, for example, WLAN, Ethernet, 4G LTE and 5G.
- Device interfaces: These interfaces allow sensors, actuators, and other devices to connect to the Edge device. These include USB, HDMI, CAN bus, RS232, or RS485.
- Communication interfaces: In connection with the hardware interfaces, the implementation must also be considered and taken into account in terms of software for a data exchange. This includes: Communication standards such as OPC-UA, Modbus, and protocols such as MQTT and CAN.
- Human-machine interfaces (HMI): These interfaces enable interaction between users and Edge gateways. They include screens, keyboards, touchscreens, and voice controls.